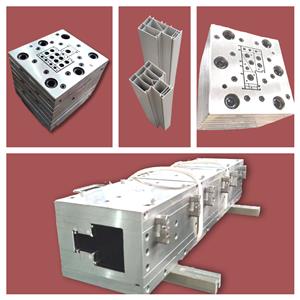
La plastica PVC, la costruzione dello stampo per estrusione, svela il velo per te
Esistono due forme di stampi comunemente usati: stampi a gradini per piastre e stampi a gradiente di sezione trasversale. Il percorso del flusso dello stampo a gradini della piastra cambia gradualmente, composto da diverse dime di bocca collegate in serie. Ogni piastra viene lavorata in una forma di contorno corrispondente, che cambia gradualmente dalla forma rotonda dell'ingresso alla forma dell'uscita desiderata. Ci sono smussi all'ingresso di ciascun blocco per completare la transizione da una forma all'altra. Questo tipo di costo di lavorazione dello stampo è basso, il canale di flusso non è ideale e generalmente non necessita di essere utilizzato come profilo principale. Il canale dello stampo a gradiente di sezione è aerodinamico, non può esserci alcuna zona di ritenzione del materiale nel canale, la fusione viene distribuita gradualmente e accuratamente a ciascuna sezione della forma di uscita dal cerchio all'ingresso e la velocità viene costantemente aumentata fino al velocità di uscita richiesta e la velocità di ciascun punto della sezione è la stessa. Per i profili in plastica in PVC con anime dello stampo complesse, l'anima dello stampo è integrata con la piastra della staffa, alcune sono fissate alla piastra della staffa mediante perni e viti di posizionamento e alcune sono incastonate sulla piastra della staffa mediante un inserto stretto. Non può essere facilmente smontato durante l'uso, perché il riassemblaggio e il debug richiedono molto tempo. Anche la derivazione del fuso viene effettuata in due modi: sul cono di derivazione e nella sezione di compressione. Lo stampo a gradiente di sezione può essere utilizzato come stampo del profilo principale. Lo stampo per estrusione di profili in plastica in PVC è la parte centrale della linea di produzione di estrusione, che comprende la filiera (nota anche come testa della filiera), lo stampo per modellare, il serbatoio dell'acqua di raffreddamento, ecc. La filiera è assemblata con la flangia sulla testa dell'estrusore mediante di una flangia e sono collegati l'anello riscaldante, la piastra riscaldante, l'alimentatore e la termocoppia. Lo stampo di modellatura e il serbatoio dell'acqua di raffreddamento sono fissati al tavolo di modellatura con viti e il tubo dell'acqua e quello del gas sono collegati. La struttura di base della matrice di estrusione è generalmente progettata come una struttura di più modelli impilati e assemblati. Pertanto, il canale di flusso dell'intero stampo è formato collegando uno dei canali di flusso in ciascun pezzo della dima, anteriore e posteriore. La piastra viene posizionata e fissata con perni e bulloni per formare una matrice di estrusione monolitica. La situazione di base è: la sezione a flusso costante della matrice di estrusione è spesso composta da una piastra forata e dalla metà anteriore del collo, e anche la metà anteriore e la seconda metà del collo sono progettate come due modelli, il collo e il piastra di transizione del collo. È anche possibile non utilizzare una piastra porosa, ma progettare la metà anteriore del canale di flusso del collo in un canale di flusso cilindrico per stabilizzare il flusso. La sezione divisa della matrice di estrusione inizia dalla seconda metà del collo e comprende il cono diviso, la piastra della staffa divisa e la piastra termoretraibile. La piastra termoretraibile può essere divisa non in un'unica cassaforma, ma insieme alla piastra preformata: una cassaforma. La sezione di formatura della matrice di estrusione comprende le seguenti dime: piastra cavità (nota anche come piastra preformata), dima di bocca (nota anche come piastra di formatura) e anima (nota anche come anima dello stampo). Per le matrici profilate più semplici, la piastra preformata viene combinata con la sagoma dell'imboccatura in un'unica cassaforma. 1. Punti chiave della progettazione della sezione trasversale del prodotto Il punto chiave della progettazione del prodotto con profilo in plastica in PVC è che lo spessore e la forma di ciascuna sezione devono essere distribuiti simmetricamente, in modo che il flusso del materiale nella testa della macchina sia bilanciato e il raffreddamento possa essere uniforme e la pressione tende ad essere equilibrata. In generale, lo spessore massimo e lo spessore minimo della parete della stessa sezione sono diversi < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1